What is Wheel Alignment and Balancing and How is it Done?
Wheel alignment (rot) and balancing (balans) are two of the most critical maintenance procedures that ensure a vehicle travels safely and comfortably. Since they are decisive factors in steering control, vehicle stability, and tire lifespan, every driver should have a good understanding of these two concepts. These settings must be checked, especially before embarking on a long journey or whenever a change is felt in the vehicle's driving characteristics. This is because an incorrectly performed wheel alignment or a neglected wheel balancing can both compromise road safety and damage other mechanical components of the vehicle.
In this content, we will detail what wheel alignment and balancing are, how they are performed, under what conditions they can be compromised, and what problems they can cause when faulty. We will also explain why these settings are important and what symptoms require an immediate check. Our goal is to enable drivers to approach their vehicles consciously and contribute to a safer driving experience.
Core Concepts: What are Wheel Alignment and Balancing?
Wheel alignment and balancing are two complementary adjustments that ensure the tires making contact with the road are correctly positioned and rotate harmoniously. Alignment refers to ensuring the steering and front suspension geometry operate at the correct angles, while balancing ensures the weight distribution of the tires is symmetrical. Thus, one deals with direction and angle, and the other deals with vibration and stability. Considering these two procedures together is the key to achieving a more stable and controlled drive.
What is Wheel Alignment?
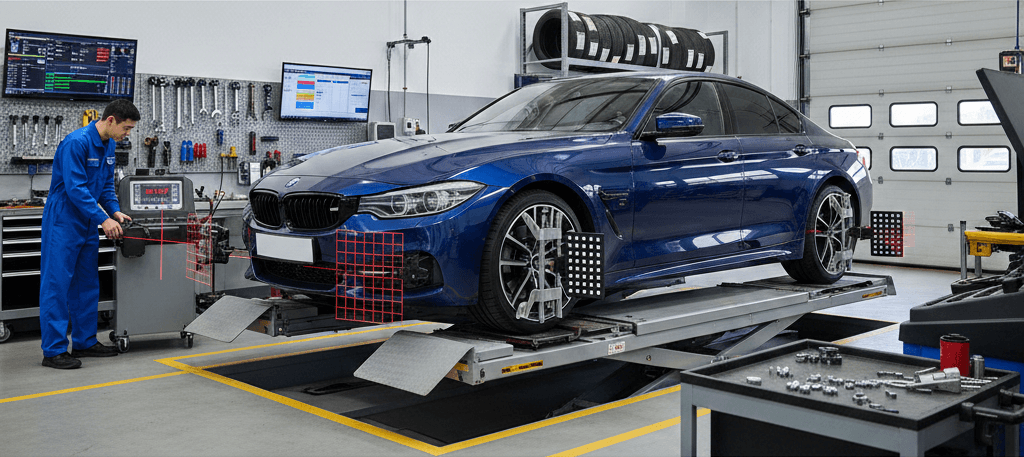
Wheel alignment is the process of adjusting the wheels in the vehicle's front end to specific factory angles. The main goal of this adjustment is to enable accurate directional tracking by ensuring the wheels rest on the road perpendicularly and parallelly. An incorrect alignment angle can cause the steering wheel to pull to one side, difficulty in driving straight, and irregular tire wear. Alignment is performed using specialized computer-aided devices, and the vehicle's angles, such as toe-in and toe-out, are measured with millimeter precision.
Damage caused by hitting potholes hard, crossing speed bumps at high speed, or bumping a curb can cause the alignment to go off. Furthermore, wear and tear in the suspension and front end components can also cause the alignment angle to change over time. Therefore, checking the alignment during every maintenance period is crucial for driving safety.
Correct alignment is not only an advantage for safety but also for fuel economy. An incorrectly angled wheel increases the vehicle's friction, causing the engine to consume more power. In the long run, this increases both tire expenses and fuel consumption.
What is Wheel Balancing?
Wheel balancing is the process of synchronizing the weight distribution of the tires and rims. The goal is to eliminate vibrations that may occur while the wheel is rotating. This is because tires and rims have minor weight differences resulting from the manufacturing process or usage. These differences can lead to severe vibrations at high speeds. During balancing, the wheel is mounted on a spinning device, and weight discrepancies are identified, prompting the addition of small weights to the rim.
When the balancing is faulty, steering wheel shudder is noticeably felt, especially in the 80–120 km/h speed range. Vibration may also occur throughout the vehicle, not just in the steering wheel. This vibration both reduces driving comfort and puts extra stress on the suspension and steering components.
Regular balancing ensures that the tires wear more evenly and healthily. Otherwise, different "spot-like" wear patterns may occur on the tire surface. This significantly reduces the tire's lifespan.
What is the Difference Between Alignment and Balancing?
Although wheel alignment and balancing are often confused, they correspond to two different procedures. Alignment focuses on the angular positioning of the wheels, while balancing deals with balancing the weight distribution of the wheels. Therefore, alignment affects the vehicle's directional stability, whereas balancing affects vibration and equilibrium.
If the alignment is faulty, the vehicle pulls to the right or left, and the tires wear internally or externally. If the balancing is faulty, the vehicle wobbles, and vibration increases, especially at high speeds. The common denominator for both adjustments is that when performed incorrectly, they negatively affect driving safety and comfort, but the mechanisms they affect are different.
In short, alignment determines "where the vehicle is going," and balancing determines "how stably it is going." Therefore, both must be checked regularly and corrected with professional equipment when necessary.
Why Is It Important? / When Should It Be Done?
Regular wheel alignment and balancing directly impact safety, comfort, tire lifespan, and the economical use of the vehicle. By preventing the vehicle from swaying, vibrating, and the tires from wearing unevenly, it protects both the driving quality and the vehicle's health. It is generally necessary to check these settings at certain intervals, during tire changes, or when abnormalities are felt while driving.
What Problems Arise When the Alignment is Faulty?
When the wheel alignment is faulty, it is noticed that the vehicle distinctly pulls to one direction. This situation causes the driver to constantly correct the steering wheel on long journeys, leading to fatigue. Furthermore, an incorrect alignment angle causes the inner or outer edges of the tires to wear rapidly. Such unbalanced wear threatens safety and increases tire expenses.
Alignment issues also negatively affect the vehicle's cornering performance. The vehicle may feel less secure in turns, and the tendency to drift may increase. Suspension and steering components also wear out faster due to this incorrect load.
Therefore, regular alignment checks are of great importance for both safe driving and economical maintenance.
What Effects Are Observed if the Balancing is Faulty?
When the balancing is faulty, vibration increases in the steering wheel and the vehicle in general, especially at certain speeds. This vibration significantly reduces driving comfort and becomes irritating on long trips. Vibration is also a factor that can damage the mechanical components of the vehicle.
Balancing issues lead to irregular wear on the tire surface. Point wear gradually degrades the tire's shape, weakening road grip. This can extend the braking distance and increase the risk of skidding in wet weather.
In addition, faulty balancing puts extra stress on the suspension, shock absorbers, and steering system. This leads to increased maintenance costs in the long run.
How Often Should Alignment/Balancing Be Performed?
It is generally recommended to check wheel alignment and balancing every 10,000 km or at least once a year. However, this period may vary depending on the vehicle's usage style, road conditions, and symptoms observed by the driver. For example, these settings may go off more frequently in vehicles that often drive on bad roads, hit curbs, or are subjected to sudden impacts.
Balancing must be done when tires are replaced. Alignment, on the other hand, should be checked when a fault is felt in steering stability, the vehicle pulls to the right or left, or unbalanced wear is observed on the tires.
Regular alignment and balancing checks both improve the overall driving quality of the vehicle and prevent potential major expenses.
Frequently Asked Questions
Are all the vehicle's wheels checked during alignment?
In most vehicles, alignment is only performed on the front wheels, but some modern vehicles have adjustable geometric points on the rear wheels as well. Therefore, all wheels are kept under control depending on the vehicle's make and model.
Does tire pressure affect alignment and balancing?
Yes, incorrect tire pressure can indirectly affect both alignment and balancing performance. Low or high air pressure distorts the tire shape, negatively impacting both angular harmony and weight distribution.
Is balancing mandatory for newly purchased tires?
Yes, balancing is mandatory every time new tires are installed. Even tires straight from the factory have small weight differences, and using them without balancing can lead to vibrations.
Can the steering wheel angle change after alignment is performed?
After a correctly performed alignment, the steering wheel becomes more stable. However, in some cases, small additional adjustments may be needed for the steering wheel to be perfectly centered. This entirely depends on the vehicle's front end geometry.
What happens if the balancing weights fall off?
The balancing weights on the rim may fall off over time due to impact. In such a case, the vehicle starts to vibrate again. Therefore, the presence of the weights should be checked periodically.